Hi!Welcome to Anruili Electronics
OR
-
 Member Center
Member Center
-
 Order Status &History
Order Status &History
-
 Address Management
Address Management
-
 RFQ History
RFQ History
-
 Favourites
Favourites
-
 Change Password
Change Password
- logout
English
Русский язык
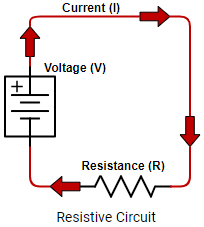
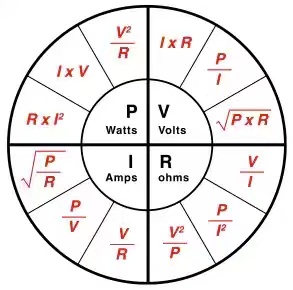
Ohm’s Law Calculator
Use DigiKey’s Ohm’s Law calculator to calculate the relationships between current, voltage, resistance, and power in simple resistive circuits. Enter at least any two input values and click calculate to solve for the remaining values. Reset the calculator after each calculation for best results.
Voltage (V)
Current (I)
Resistance (R)
Power (P)
 SMD Capacitor code
SMD Capacitor code Calculator
 Low Pass/High Pass Filter
Low Pass/High Pass FilterCalculator
 Low Pass/High Pass Filter
Low Pass/High Pass FilterCalculator
 See All Calculators
See All Calculators
Ohm’s Law Explained
Ohm’s law relates that the voltage difference between two points, the electric current flowing between them, and the resistance of the path of the current are all proportional and related to each other.
Ohm's Law explains the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance by stating that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points.
This can be expressed mathematically in the following equations in terms of V the voltage difference, I the current in amperes, and R resistance in ohms.
What this means in practical terms is that the current passing across a two-terminal device like a resistor with a fixed value of resistance is directly related to the voltage difference applied across the terminals.
The law states that That means for a given constant voltage, higher resistance entails lower current flow. And the reverse is also equally true, for the same given constant voltage, lower resistance would mean higher current flow.
Examples
The voltage V in volts (V) is equal to current I in amps (A) multiplied by the resistance R in ohms (Ω):
So, for a circuit with 5 ohms (Ω) of a resistance that needs 3 amp (A) of current to function, the voltage required would be 15V.
The power dissipated by the circuit can also be found using the values in Ohm’s Law. For example, the power P in watts (W) is equal to the voltage V in volts (V) times the current I in amps (A):
For a circuit with 20 volts (V) and a current of 2 amps (A) the total power is 40 watts (W).